Contents
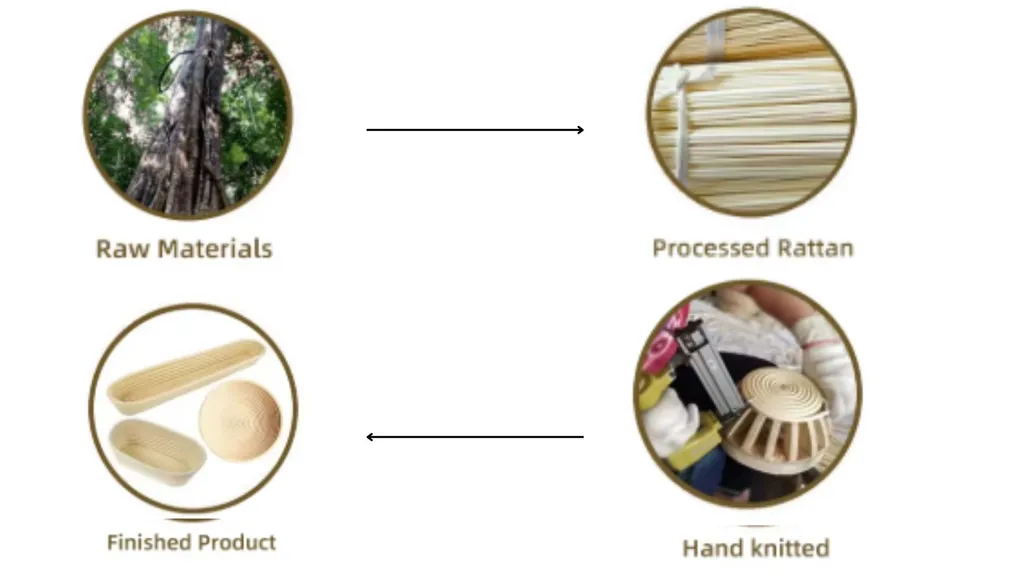
Exploring the world of rattan processing opens the door to understanding how this versatile natural material transitions from its raw, untamed state to a polished, functional piece of craftsmanship. Often overshadowed by other materials like wood or synthetic composites, rattan possesses unique qualities of strength and flexibility, making it a significant contender in furniture-making and decorative arts. This exploration delves into the meticulous selection of rattan materials, harvesting methods, processing techniques, and quality controls that encapsulate its journey from wild vine to elegant item. The narrative does not just celebrate rattan’s transformation but also applauds the commitment to sustainability, innovation, and traditional craftsmanship that defines this industry. As we embark on this detailed journey, prepare to uncover the complexities and artistry entwined in each stage of rattan processing. Each section meticulously paints a picture of the processes involved, offering insights into traditional and modern approaches and highlighting the impacts on ecology and economy alike.
Selecting Quality Rattan
The foundation of superior rattan products lies in careful material selection. Manufacturers evaluate rattan based on key criteria to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal:
Diameter and Length: Rattan with diameters over 1.5 cm is ideal for sturdy furniture, balancing strength and visual appeal.
Color Consistency: Uniform natural hues ensure cohesive, high-quality products.
Flexibility and Strength: Rattan must be pliable for weaving yet strong for durability.
Growth Conditions: Sustainably harvested rattan from well-managed forests ensures better quality and environmental responsibility.
Key rattan types include:
Vietnamese Rattan: Flexible and aesthetically appealing, ideal for furniture and decor, with over 40 species supporting sustainable cultivation.
Indonesian Rattan: Dense and durable, perfect for heavy-duty furniture, though export regulations favor semi-finished products.
Philippine Rattan: Lightweight and smooth, suited for intricate weaving, but limited by overharvesting.
Thai Rattan: Artisanal and high-quality, focused on handcrafted, high-end designs.
Chinese Rattan: Cost-effective but requires careful quality control due to intensive processing.
Harvesting Rattan Sustainably
Rattan harvesting blends tradition with modern efficiency to ensure sustainability and quality.
Traditional Methods: Farmers identify mature canes by skin color and flowering, using machetes to cut carefully and preserve younger shoots. Post-harvest, leaf sheaths are removed within 24 hours to maintain quality.
Modern Practices: Sustainable extraction, aided by machinery and hot water treatments, reduces pests and enhances durability. Advanced quality checks ensure market-ready materials.
These methods balance ecological preservation with efficient production, ensuring a steady supply of high-quality rattan.
Processing Rattan
Processing transforms raw rattan into versatile materials through a series of precise steps:
Stripping and Soaking: Removing the outer skin and soaking in water enhances flexibility for shaping.
Drying: Air or kiln drying removes moisture, preserving structural integrity.
Curing: Boiling in oils (80–150°C) reduces moisture, deters pests, and boosts durability. Dyeing adds aesthetic appeal with natural or synthetic hues.
Sorting: Rattan is sorted by size and quality, ensuring consistency for specific applications.
Bending and Shaping: Soaking and steam application enable intricate designs, with molds ensuring uniform shapes for furniture and decor.
Finishing: Sanding, varnishing, and sealing enhance texture, durability, and visual appeal, protecting against environmental wear.
Sustainability in Rattan Processing
Sustainability is central to rattan production. Responsible harvesting preserves ecosystems, while local craftsmanship supports communities and reduces environmental impact. Rattan serves as a renewable alternative to timber, stabilizing soils and supporting biodiversity. The industry, valued at over $1.7 billion, drives economic growth in rural areas, blending tradition with eco-conscious innovation.
Quality Control and Applications
Rigorous quality control ensures rattan products meet high standards. Inspections check for defects, moisture levels, and structural integrity, adhering to benchmarks like ISO 23067:2022. Processed rattan shines in:
Furniture: From sleek dining chairs to durable outdoor tables.
Decor: Intricate wall hangings, room dividers, and artisanal crafts.
Sustainable Design: Eco-friendly textiles and architectural elements.
Trends in Rattan Design
Rattan continues to evolve, driven by:
Eco-Conscious Demand: Consumers favor renewable, sustainable materials.
Technological Innovation: Advanced processing enables customized, modern designs.
Biophilic Design: Rattan integrates nature into interiors, blending aesthetics with functionality.
Crafting Excellence with Ethical Handicraft Manufacturer
Rattan’s journey from raw material to finished product showcases a blend of tradition, innovation, and sustainability. At Ethical Handicraft Manufacturer (EHM), we embody these values, delivering high-quality, eco-friendly rattan products that elevate spaces while supporting sustainable practices. Discover our craftsmanship at handicraftmanufacturer.com.





